
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is Amazon’s Cloud infrastructure platform. It delivers similar tools and services to those available from Microsoft Azure. One of the central services offered in AWS is Amazon EC2; this is Amazon’s method of providing scalable virtual servers on demand from an Elastic Cloud, hence the name EC2. It’s simple and cost effective to deploy however many server instances required via the EC2 web interface. These servers can run any of the popular operating systems in use today.
When Microsoft Windows Server is deployed as the operating system on EC2 virtual machines, then any of the Microsoft business server applications can be installed, including Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 through to the latest 2016 version
Key Features of Deploying Exchange on AWS
Deploying Windows Server and Exchange Server on EC2 based infrastructure provides all the benefits associated with Cloud delivery, including the ability to quickly scale the compute and storage capacity up and down as needs change. Here are some of the key features and benefits that come along with AWS EC2 deployment:
- No upfront capital outlay for initial or future servers.
- Easy to start implementation with just the server instances required, and then scale up quickly if capacity needs to be enhanced.
- Easy, automated deployment of virtual machines via a simple Web-based interface and template-based workflows.
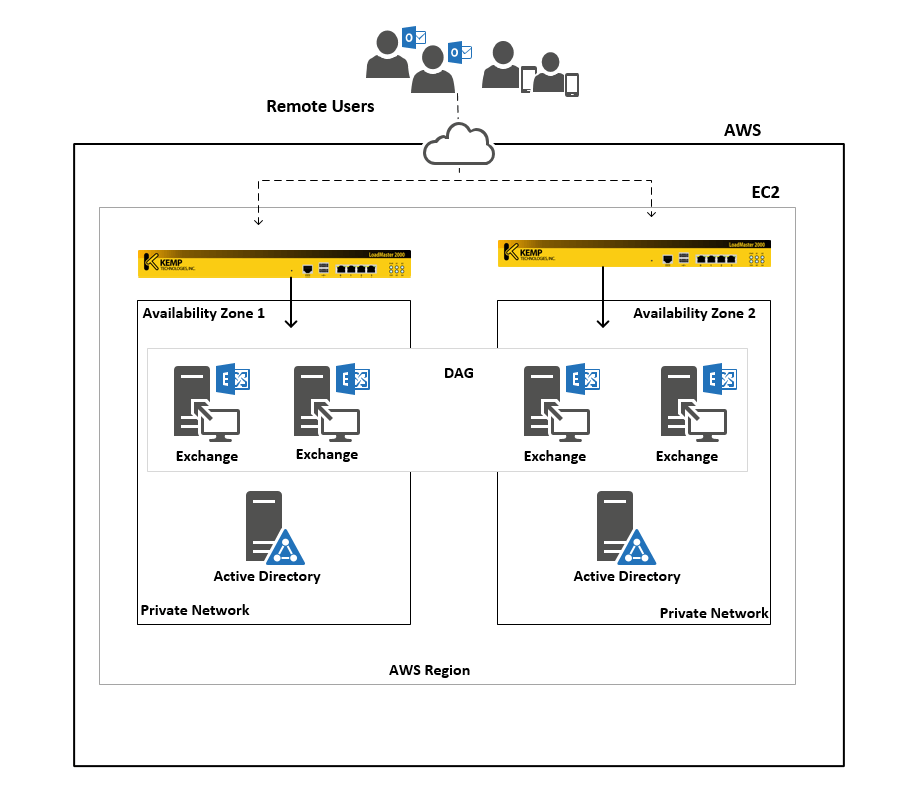
- Provides full load balancing with Kemp LoadMaster for AWS to provide high availability and Site Resilience. LoadMaster can work in conjunction with and enhance the following AWS features:
- High Availability with the AWS Availability Zone functionality.
- Site Resiliency across the zone within the AWS region
- Exchange High Security and compliance features are fully available when deploying on EC2.
- The Microsoft Preferred Architecture for Exchange Server deployments can be fully realised when deploying on EC2 hosted virtual machines.
- Complete control of the Exchange servers and environment.
How the deployment works
Deploying Microsoft Exchange Server to AWS EC2 is done with the same planning and design stages as an on-premises deployment. A summary of this process is given below:
- all the requirements and users profile information for the deployment.
- Use Exchange Role Requirement Calculator to input all the design requirement and user profile information.
- Determine the CPU specifications needed from requirements calculator and design the servers needed with High Availability and Site Resiliency in mind.
- Based on design, deploy virtual servers in a Zone within Amazon EC2.
- Install and configure Exchange Server on the virtual machines and configure High Availability using DAG settings.
- Deploy a Kemp LoadMaster Load balancer in First zone and configure High Availability for Exchange services.
- Deploy Virtual Servers in a second Zone in the same AWS region to provide Site resilience.
- Install and Configure Exchange servers on virtual machines in the second Zone and configure site resiliency using DAG settings.
- Deploy a Kemp LoadMaster Load balancer in the second zone and configure High Availability for Exchange services.
 AWS is an ideal replacement for Exchange Server on premise deployments. It provides the server, storage, and site infrastructure needed to implement Microsoft’s preferred architecture on Exchange database resilience. AWS also delivers all the other resources required for successful deployment. Kemp LoadMaster for AWS integrates seamlessly into AWS EC2 deployments, giving you the best Cloud infrastructure from Amazon and the best Application Delivery Controller and load balancer from Kemp Technologies.
AWS is an ideal replacement for Exchange Server on premise deployments. It provides the server, storage, and site infrastructure needed to implement Microsoft’s preferred architecture on Exchange database resilience. AWS also delivers all the other resources required for successful deployment. Kemp LoadMaster for AWS integrates seamlessly into AWS EC2 deployments, giving you the best Cloud infrastructure from Amazon and the best Application Delivery Controller and load balancer from Kemp Technologies.
