
Load Balancer settings when migrating from Exchange Server 2013 to Exchange Server 2016
When performing this migration both versions of Exchange Server will need to coexist on the network. To do this Microsoft Exchange Server 2013 must be running Cumulative Update 10 (CU10) or later. If you have not updated your Exchange Server 2013 infrastructure to CU 10 then you must do this before introducing Exchange Server 2016 if you want them to work together.
The load balancer setup plays a vital role in client connections to Exchange Server. It helps establish the connection from the client to the Exchange Client Access Server (CAS) servers, which run the client connection service, and distributes the client connection load across the multiple backend Exchange servers. Load balancers have various mechanism to check the health and availability of target CAS servers and establishes the connection to the most suitable one at any given time.
Configuring the Load Balancer when Migrating from Exchange 2013 to Exchange 2016
When organizations are migrating from Exchange 2013 to Exchange 2016, it may take some time to complete the project. As a result, it is essential to configure the previous and new Exchange systems to coexist. A correctly configured load balancer setup can make this possible.
There are various protocols that clients use to connect to the Exchange server. They are:
- Outlook Web App (OWA)
- Autodiscover
- Exchange Web services (EWS)
- Exchange Active Sync(EAS)
- Offline Address book (OAB)
- Outlook Anywhere
- MAPI
- SMTP Protocol
| Virtual Directory | Internal URL | External URL |
|---|---|---|
| OWA Virtual Directory | https://mail.domain.com/OWA | https://mail.domain.com/OWA |
| ECP Virtual Directory | https://mail.domain.com/ECP | https://mail.domain.com/ECP |
| OAB Virtual Directory | https://mail.domain.com/OAB | https://mail.domain.com/OAB |
| WebService Virtual Directory | https://mail.domain.com/EWS/Exchange.asmx | https://mail.domain.com/EWS/Exchange.asmx |
| ActiveSync Virtual Directory | https://mail.domain.com/Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync | https://mail.domain.com/Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync |
| MAPI Virtual Directory | https://mail.domain.com/MAPI | https://mail.domain.com/MAPI |
| AutoDiscoverServer Internal URI | https://autodiscover.domain.com | https://autodiscover.domain.com |
| Outlook Anywhere | http://mail.domain.com |
Figure 1 shows a typical Exchange 2013 deployment with a load balancer.

Exchange Organizations after introducing Exchange 2016
As servers running Exchange 2016 Server are introduced into an organization the same CAS URLs and name space from Exchange 2013 can be used. This configuration helps the coexistence between Exchange Server 2013 and Exchange Server 2016 as it uses the same URL Mail.domain.com for all the client connections.
Figure 2 shows a typical deployment model for Exchange Server 2013 and Exchange Server 2016 coexistence. The Exchange Server 2016 servers need configured to work with the URL’s Mail.domain.com and Autodiscover.domain.com that are in use on Exchange Server 2013. This allows all the clients to connect to Exchange Server 2016, and if the user mailbox is on Exchange 2016, then the CAS service directly proxies the connection to the user’s mailbox. If the target mailbox is on an Exchange Server 2013 host then Exchange Server 2016 CAS service redirects the request to the Exchange Server 2013 mailbox server.
If the Exchange Server CAS connection is managed using the load balancer then no DNS changes are required as the load balancer can be configured to redirect all the new connections to Exchange 2016 server. Load balancers can also be configured to route SMTP traffic to Exchange Server 2016 based on the mailbox server location.
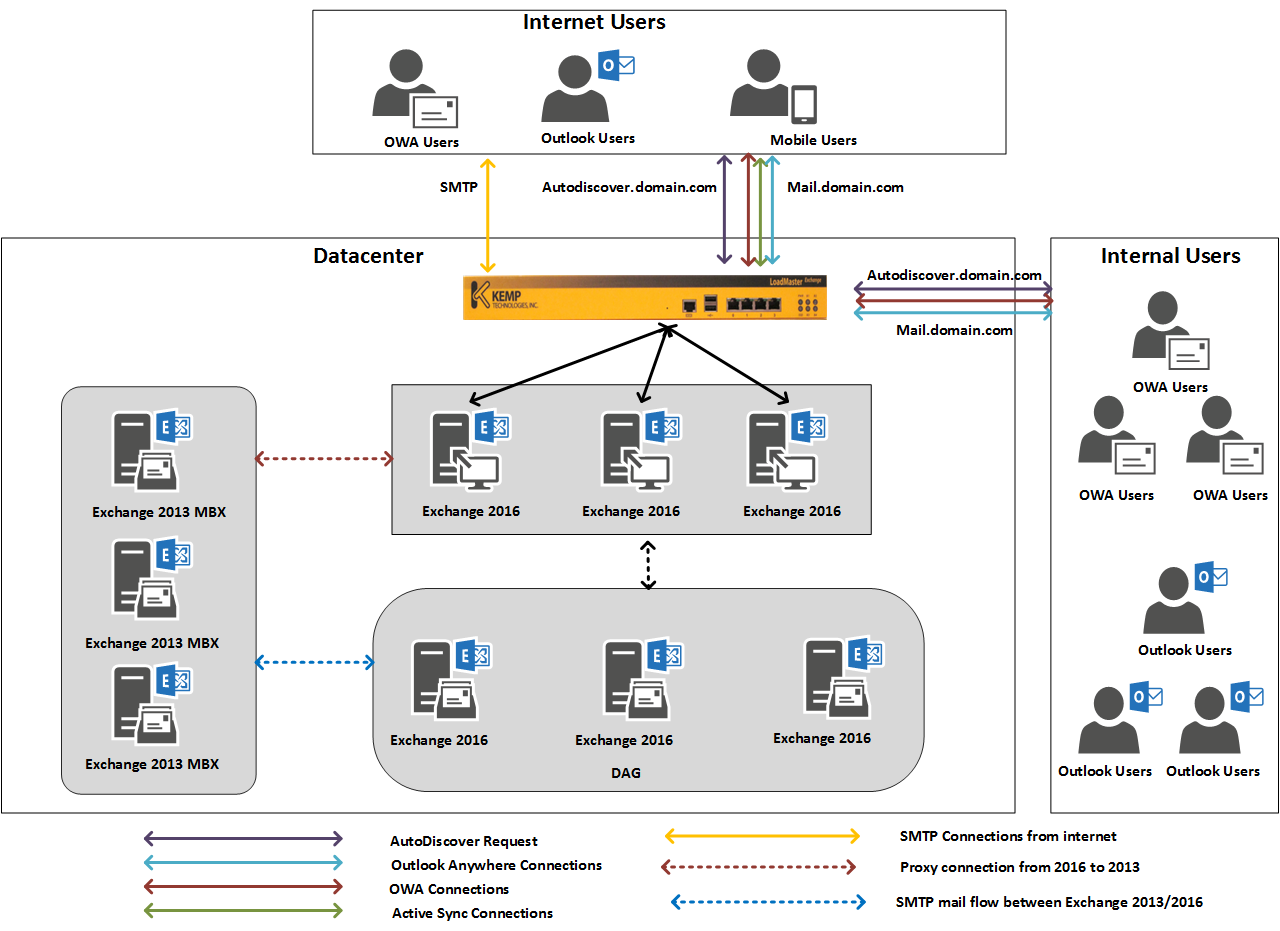
The points below outline how various protocols are proxied from Exchange 2013 to Exchange 2016:
Autodiscover
Outlook -> Exchange 2016 -> Authenticates -> Determines the mailbox location -> Retrieves the configuration details of Mailbox Exchange 2013 or Exchange 2016 depending on the target mailbox location.
Outlook Anywhere
Outlook -> Exchange 2016 -> Authenticates -> Determines mailbox location -> Proxies Connection -> Exchange 2013/2016 Mailbox.
Offline address book
Outlook -> Exchange 2016 -> Authenticates -> Determines the mailbox location -> Retrieves the configuration details of Mailbox Exchange 2013 or Exchange 2016 depending on the target mailbox location -> share to the connection URL to the client.
OWA Protocol
OWA Client -> Exchange 2016 -> authenticates -> Proxies/redirect Connection -> Exchange 2013/2016 Mailbox.
Active Sync Protocol
Active Sync Client -> Exchange 2016 -> Authenticates -> Determines mailbox location -> Proxies Connection -> Exchange 2013/2016 Mailbox.
Exchange Web Service
Exchange Web Service Client -> Exchange 2016 -> Authenticates -> Determines mailbox location -> Proxies Connection -> Exchange 2013/2016 Mailbox.
