Azure and Cloud Load Balancing: Unleashing the Power of a Load Balancer in Azure
.png?sfvrsn=91d74074_1)
Deploying applications to cloud services has become the default choice for many organizations. Cloud deployment’s flexibility and elastic scalability have helped revolutionize multiple business sectors. Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform is a popular choice for organizations using the Microsoft Server technology stack. Microsoft has made it straightforward to extend applications built on their stack to Azure.
Navigating the Cloud Load Balancing Landscape
As workloads and applications get deployed fully or partially in the cloud, availability and performance must be front and center in planning and deployment strategies. Crucial to this is using a load balancing application to manage the load across virtual machines, cloud data centers and geographic regions. You have several choices when load balancing web applications and other solutions deployed to Azure.
Azure Load Balancing Options
Microsoft provides Azure load-balancing options and an application gateway service within the Azure platform. We outline these options later and discuss why Progress Kemp LoadMaster for Azure could be a good option if your organization is looking to get the maximum from Azure application investments.
Understanding Azure Load Balancing
The load balancing options Microsoft provides natively within Azure may meet your cloud load balancing requirements when you are looking to optimize your Azure traffic distribution.
Azure Load Balancer
The core Azure Load Balancer is a Layer 4 service that supports Azure traffic distribution across multiple virtual machines or cloud services. It supports inbound and outbound configurations, enabling the management of traffic flows in both directions. Plus, it can load balance applications and services that operate wholly within Azure in addition to load balancing applications for users accessing them from outside Azure. It offers the following features:
Traffic distribution - Azure Load Balancer distributes incoming traffic across multiple backend servers or instances to minimize overloading and maintain optimal performance.
Health monitoring - Azure Load Balancer monitors backend server health and redirects traffic away from any servers with issues to reduce service disruptions.
Session affinity - Azure Load Balancer can maintain session affinity, directing requests from a particular client to the same backend server. This helps enhance the user experience and supports application performance for requests that benefit from using an optimized server. Video streaming is one example of this.
Scalability - Organizations can scale Azure Load Balancer more easily to meet their changing traffic demands, providing flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Azure Load Balancer supports several load balancing algorithms, such as Round-Robin, source IP affinity and port-based affinity. By choosing the appropriate algorithm, your IT team can optimize traffic distribution based on your organization’s application requirements. You can learn more on Microsoft’s Azure Load Balancer webpage.
Azure Load Balancer vs. Azure Application Gateway: Making the Right Choice
Microsoft, in addition to the Layer 4 network traffic Azure Load Balancer, also provides an Application Gateway service. This is a Layer 7, or application layer, load balancer that offers features such as TLS/SSL termination, URL-based routing, cookie-based session affinity, hybrid public/private websites and a web application firewall (WAF).
Choosing between the Native Azure Load Balancing Options
Choosing whether to use Azure Load Balancer or Azure Application Gateway depends on the workloads your organization has deployed and any application-specific requirements you have. If basic load balancing is enough, Azure Load Balancer is a cost-effective and efficient solution. However, if advanced features like TLS/SSL termination or URL-based routing are necessary, Azure Application Gateway (or a third-party alternative like LoadMaster for Azure) will be required.
You can find more information on Microsoft’s more advanced Azure load balancing option on the Microsoft Application Gateway page.
Optimizing Azure Traffic Distribution with Load Balancer Configurations
To successfully load balance in Azure it is crucial to correctly configure the load balancer. Choosing an algorithm or server monitoring service to meet the specific needs of your applications or network services will impact performance and resilience. Furthermore, by using multiple availability sets and virtual networks, it is possible to increase fault tolerance and isolate traffic types to improve your overall service performance.
Doing this can be complex and requires that IT teams have more in-depth knowledge of how the Azure Load Balancing choices work. These hard-won skills are limited to use within the Azure platform. Other cloud services and on-premises deployments will require different load-balancing skills. LoadMaster can bridge this multi-service and multi-cloud skills gap by allowing the use of the same load balancing solution across your cloud and on-premises deployments.
Benefits of Load Balancing in Azure
Load balancing in Azure is critical to the effective delivery of applications and services from the platform. Just because parts of your infrastructure are now deployed in the cloud doesn't mean that responsibility for optimizing for performance is shifted to Microsoft. Whichever load balancer solution you use, it will provide several cloud load balancing benefits.
High Availability – Increase the accessibility of applications and services, even after failures or during planned maintenance. This level of reliability is crucial for businesses looking to build more resilient systems in the cloud, and the Azure load balancing options can deliver that when appropriately configured.
Scalability – A good load balancer enables organizations to handle increased traffic loads. This amplifies resource utilization and decreases bottlenecks and performance degradation as your business grows and experiences higher demand.
Deployment flexibility - A proper load balancer enables load balancing for virtual machines and cloud services, providing flexibility to manage various workloads—whether in Azure or not. This capability is advantageous for businesses with hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Additionally, deployed resources are used effectively, which helps lower operational costs.
Performance improvements - By evenly distributing traffic across multiple servers, a load balancer reduces latency and helps improve application responses to user requests.
Best Practices for Cloud Load Balancing Strategies
Realizing the benefits of cloud load balancer options requires you to configure the deployed services correctly. Here are some best practices organizations should follow when using Azure load balancing services (or other load-balancing solutions!)
Design Best Practices
Design for high availability - Distribute workloads and application servers across multiple availability zones or regions to help strengthen resilience against local and regional failures.
Plan for session affinity - Use session affinity when possible to maintain a consistent user experience and enhance application performance.
Management Best Practices
Monitor traffic patterns- Regularly analyze traffic patterns to identify trends and potential bottlenecks, thereby enabling proactive load balancer adjustments. Scale load balancing resources to avoid performance degradation.
Enable logging and diagnostics – Taking advantage of logging and diagnostic capabilities provides insights into load balancing performance, enabling proactive troubleshooting. Upgrade server health checks to improve detection and response capabilities.
Security Best Practices
Use security features - Deploy features like a Web Application Firewall (WAF) and SSL offloading to better safeguard your applications against threats and improve your overall security posture.
Use available security features - Implement network security groups and access control lists to better secure load-balancing resources.
Load Balancing in Azure with LoadMaster
While the Azure Load Balancer and Azure Application Gateway may meet the needs of many organizations, there are certain downsides to using them. As previously mentioned, configuring these tools requires technical skills. These hard-won skills are primarily specific to the Azure platform—with some overlap common to all load-balancing solutions.
Plus, many organizations now use multiple cloud providers and on-premises servers in hybrid deployments. Having multiple different load balancing solutions focused on each cloud platform and server stack increases complexity, makes cybersecurity and management harder, raises operating costs and greatly minimizes the big-picture view.
A third-party load balancing solution such as LoadMaster works in the same way, with the same toolset and interface, but across different cloud providers and on-premises deployments. It enables IT specialists to become experts in one prominent load-balancing solution that works across the platforms your organization uses.
LoadMaster for Azure
LoadMaster for Azure provides L4-7 load balancing and application delivery services. It delivers intelligent global traffic distribution capabilities that support hybrid deployments between Azure and private cloud environments while enabling continuous application performance across cloud boundaries. It can be deployed directly from both the Azure Marketplace and the Azure Marketplace for Government.
LoadMaster for Azure delivers numerous features and functionality that a combined deployment of Azure Load Balancer and Azure Application Gateway offers. However, LoadMaster for Azure also provides the support our customers have enjoyed over the years for their on-premises deployments. The following table (from the Load Balancing in Microsoft Azure page) compares LoadMaster for Azure with both Microsoft offerings.
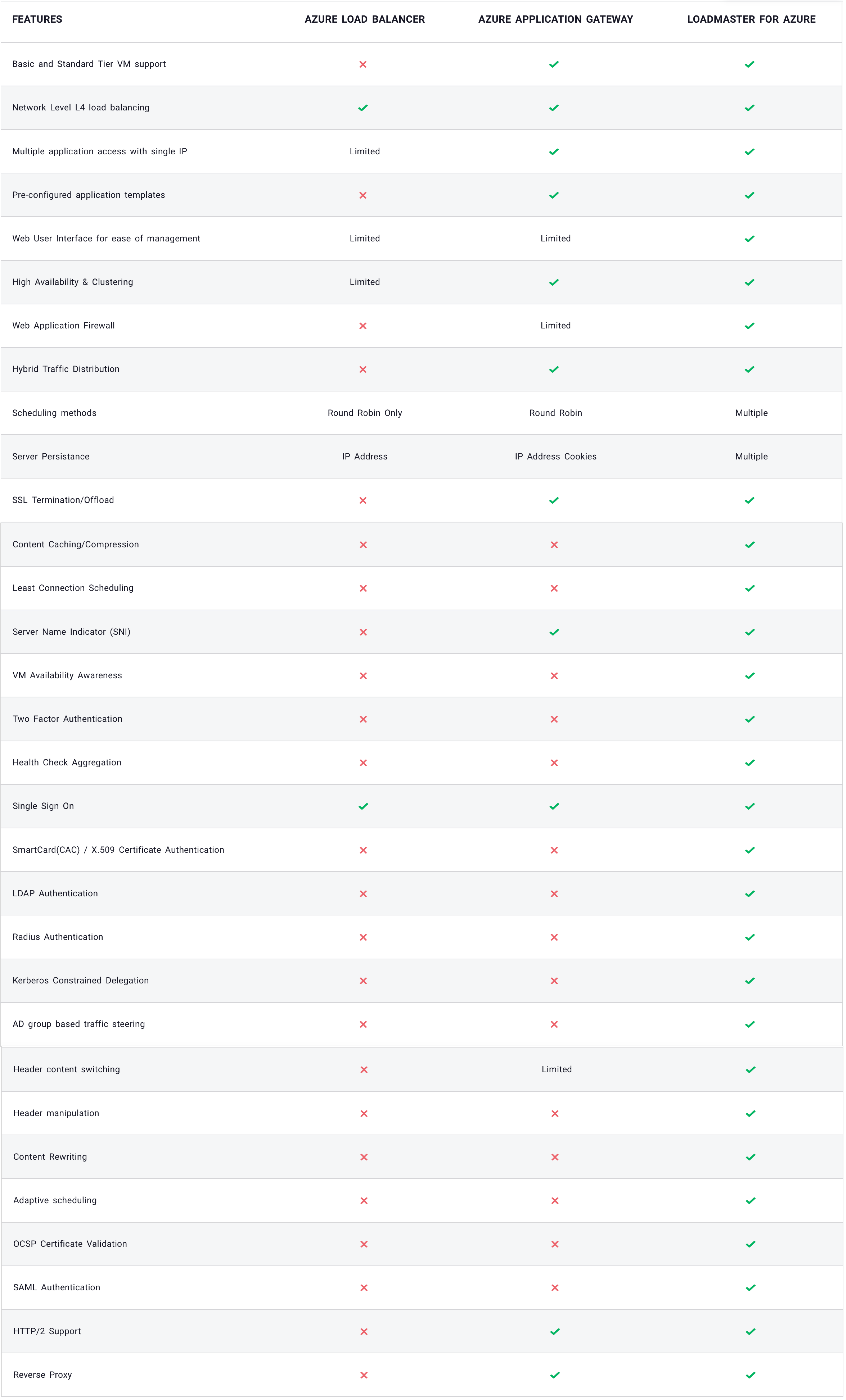
Conclusion
Azure Load Balancer and Azure Application Gateway provide crucial components for your organization when deploying to Azure. Because they are highly available, scalable and flexible, their reliability is increased. However, configuring them requires skilled systems administrators, and these skills will be specific to the Azure load balancing options.
LoadMaster for Azure provides equivalent and additional features to Microsoft’s offerings while enabling system administrators to use their skills across multiple cloud platforms and on-premises deployments. The LoadMaster solution provides a unified big-picture view of load balancing across your multi-cloud and hybrid infrastructure deployments.
Learn more about Azure load balancing with LoadMaster at https://kemptechnologies.com/azure, and don’t hesitate to contact us for advice on Azure load balancing solutions.
References
Progress Kemp: Load Balancing in Azure - https://kemptechnologies.com/azure
Microsoft: Azure Load Balancer - https://azure.microsoft.com/services/load-balancer/
Microsoft: Application Gateway - https://azure.microsoft.com/products/application-gateway/

Doug Barney
Doug Barney was the founding editor of Redmond Magazine, Redmond Channel Partner, Redmond Developer News and Virtualization Review. Doug has also served as Executive Editor of Network World, Editor in Chief of AmigaWorld and Editor in Chief of Network Computing.
more from the author