Always On VPN Redundancy and Failover with KEMP LoadMaster GEO
Introduction
When implementing Windows 10 Always On VPN, eliminating single points of failure is crucial to ensuring the highest levels of productivity for mobile workers. Enabling load balancing for VPN servers in a single location can prevent outages in the event of an individual server failure, but it does not provide any geographic redundancy or failover.
Manual Failover
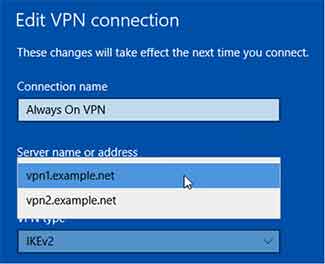
Entering multiple Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) is possible when creating an Always On VPN connection in Windows 10. However, this does not provide automatic failover as you might expect. The client will always connect to the first VPN server in the list and will not load balance or automatically failover to another site. To failover to another VPN server, the user must modify the settings of the VPN connection and manually select a different VPN server to connect to.

Automated Failover
To enable automatic failover and intelligent site selection, a Global Server Load Balancer (GSLB) such as the KEMP LoadMaster GEO must be deployed. Using GEO, administrators can configure VPN clients with a single FQDN for remote access connections. GEO will monitor back end VPN servers and ensure that client connections are always routed to VPN servers that are available. Administrators can further tailor GEO settings to balance connections between locations, direct all connections to a primary location and failover to another if the primary is unavailable, or route VPN connection requests to the nearest VPN server based on their location.
GEO Configuration
Note: Before configuring GEO the administrator must decide on the FQDN to be used by VPN clients. In addition, a DNS delegation must be created in public DNS to forward queries to the GEO appliance. Configuration guidance for KEMP LoadMaster GEO can be found here.
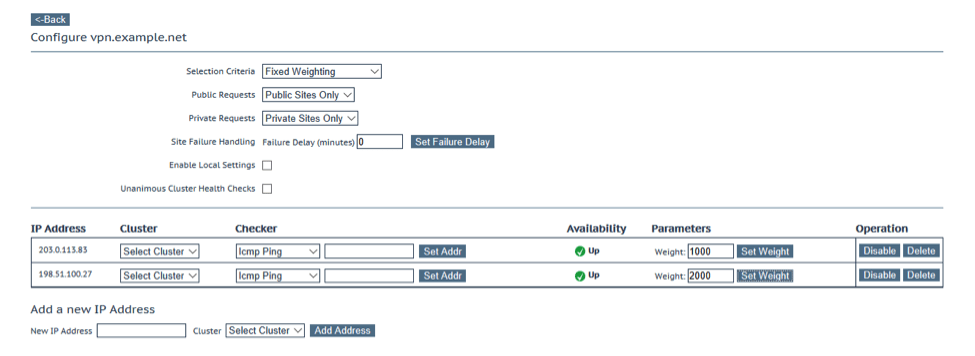
To configure GEO for Always On VPN geographic load balancing for two VPN servers in different physical locations, open the KEMP LoadMaster GEO web user interface and perform the following steps.
1. Expand Global Balancing.
2. Click Manage FQDNs.
3. Enter the FQDN to be used by VPN clients.
4. Click Add FQDN
5. Choose an appropriate scheduling method from the Selection Criteria dropdown list. 6. Choose an appropriate DNS query response policy from the Public Requests dropdown list. 7. Choose an appropriate DNS query response policy from the Private Requests dropdown list. 8. Enter the public IP address of the VPN server in the New IP Address field. 9. If the KEMP GEO is part of a cluster, select the appropriate device from the Cluster dropdown list. 10. ClickAdd Address. 11. Repeat these steps for each additional VPN server as necessary.
Summary
Native Windows 10 Always On VPN connections provide no useful failover or redundancy options. To ensure that clients can connect to a VPN server that is online, KEMP GEO can be configured. This allows administrators to define a single FQDN for VPN client connections, which improves availability and provides additional deployment flexibility as well.
